

Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-10-22 Origin: Site











Transformer cores are essential components in electrical systems, ensuring the efficient transfer of energy. They act as a conduit for magnetic flux, allowing electricity to flow safely and effectively from power plants to homes and industries. Without transformer cores, energy transmission would be inefficient and costly.
In this article, we will explore how transformer cores are used worldwide, their types, materials, and their applications in both traditional and renewable energy systems. You'll also learn about their environmental impact and innovations driving future advancements.
Transformer cores are key players in the process of power generation and transmission. They are primarily used in power plants to step up and step down voltages, ensuring the efficient transmission of electricity over long distances. High-voltage transmission lines are essential for reducing energy loss during transportation, as higher voltage allows for the transmission of electricity at lower currents, minimizing heat losses due to resistance in the wires.
The transformer core is responsible for ensuring that the voltage is adjusted appropriately to match the needs of both the power transmission network and the receiving end. This voltage adjustment helps maintain stability in the grid and optimizes energy flow across vast distances, particularly in large-scale power plants.
Once electricity is transmitted at high voltage over long distances, transformer cores play a crucial role in reducing voltage for safe distribution to consumers. In local substations, transformer cores are used to step down the voltage, making electricity safe for homes, industries, and businesses. This process is crucial for maintaining safety standards and ensuring that electrical devices operate correctly without risking overloads or electrical accidents.
These transformers ensure that power is delivered efficiently and in a controlled manner, providing a steady supply of electricity that meets the demands of urban areas, rural communities, and industrial sectors alike.
When selecting transformer cores for distribution systems, ensure that they are designed to minimize energy losses while providing the required mechanical strength to handle long-term operational stresses.
Core-type transformers are widely used for high-voltage applications, particularly in power transmission networks. These transformers feature windings placed around a rectangular core, which helps direct the flow of magnetic flux efficiently. The core-type transformer design is most effective in situations where the transformer needs to handle significant amounts of power, such as in high-voltage substations and transmission lines.
One of the key benefits of core-type transformers is their ability to provide an efficient magnetic flux path, making them highly suitable for large-scale power generation and distribution systems. These transformers are often seen in power plants, where the step-up transformer cores ensure the transmission of electricity at high voltage levels.
Shell-type transformers are used for lower-voltage, high-current applications, such as industrial power supplies and certain types of distribution transformers. Unlike core-type transformers, shell-type transformers enclose the windings in a core that surrounds them. This design enhances mechanical strength and reduces magnetic leakage, making shell-type transformers ideal for applications requiring high short-circuit strength and improved voltage regulation.
Shell-type transformer cores are commonly used in situations where durability and the ability to withstand high fault currents are necessary. Their design also offers benefits in terms of reducing energy losses and improving performance in specific environments, such as factories and heavy machinery applications.
Toroidal transformers, characterized by their donut-shaped core, are compact and efficient. These transformers are particularly effective in situations where space is limited, such as in electronics, audio equipment, and computer power supplies. Toroidal transformer cores minimize electromagnetic interference, making them ideal for sensitive electronics that require precise power conversion without signal distortion.
Their design also reduces the amount of material required compared to other transformer types, making them a cost-effective solution in small-scale applications while still offering efficient energy transfer.
Core Type | Design Characteristics | Typical Use Cases |
Core-Type | Windings surround a part of the core, suitable for high-voltage | Power transmission, high-voltage systems |
Shell-Type | Core surrounds windings, suitable for low-voltage, high-current | Distribution transformers, industrial power supplies |
Toroidal | Compact, circular design, high energy transfer efficiency | Electronics, small appliances, audio equipment |
Silicon steel is the most commonly used material for transformer cores worldwide. Its high magnetic permeability and low energy loss make it an ideal choice for power transformers in power plants, substations, and distribution networks. Silicon steel is used because of its ability to handle large amounts of electrical energy with minimal losses, ensuring that transformers operate efficiently over long periods.
Silicon steel is typically used in grain-oriented form (GO), where the steel’s crystal structure is aligned to reduce hysteresis loss. This material is widely used in high-voltage transformers due to its ability to efficiently conduct magnetic flux.
Amorphous metals, also known as non-crystalline metals, have a unique atomic structure that helps reduce both hysteresis and eddy current losses. These materials are especially beneficial in energy-efficient transformer cores, as they minimize energy losses significantly compared to traditional silicon steel.
Amorphous steel cores are used primarily in distribution transformers, particularly in applications where energy efficiency is a priority. These materials are especially effective in renewable energy applications and small transformers, where reducing energy waste is critical to achieving long-term sustainability.
Ferrites and other specialized materials are used in high-frequency applications, such as electronics, switch-mode power supplies (SMPS), and small transformers. Ferrites, made from iron oxide and other metal elements, have high electrical resistivity, which helps minimize eddy current losses. These materials are most commonly found in transformers used in high-frequency applications where efficiency is paramount.
For transformers used in electronic devices or SMPS, consider ferrite-based cores to minimize energy loss and maximize performance at high frequencies.
Material | Properties | Common Applications |
Silicon Steel | High permeability, low energy loss | Power grids, large transformers |
Amorphous Metals | Ultra-low core losses, energy-saving | Renewable energy, high-efficiency transformers |
Ferrite | High electrical resistivity, reduces eddy currents | High-frequency transformers, electronics |
Nanocrystalline | Even lower losses than amorphous, higher saturation flux density | Specialized high-efficiency designs |
Transformer cores are at the heart of efforts to reduce energy waste in power systems. High-quality transformer cores, made from materials like grain-oriented silicon steel and amorphous metals, minimize core losses, which include both hysteresis and eddy current losses. By reducing these losses, transformer cores improve the overall efficiency of the electrical grid and contribute to energy savings.
The global push for energy conservation and sustainability has driven significant improvements in transformer core materials and design. More efficient transformer cores help reduce operational costs, decrease environmental impact, and contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
The choice of materials in transformer cores directly impacts their environmental footprint. Amorphous metal cores, which significantly reduce core losses, are often chosen for energy-efficient transformers, helping manufacturers comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. By reducing energy losses, these transformers also contribute to the reduction of carbon emissions in power distribution networks.
Tip: Choose transformer cores made from low-loss materials to meet environmental standards and enhance energy savings over the transformer’s lifecycle.
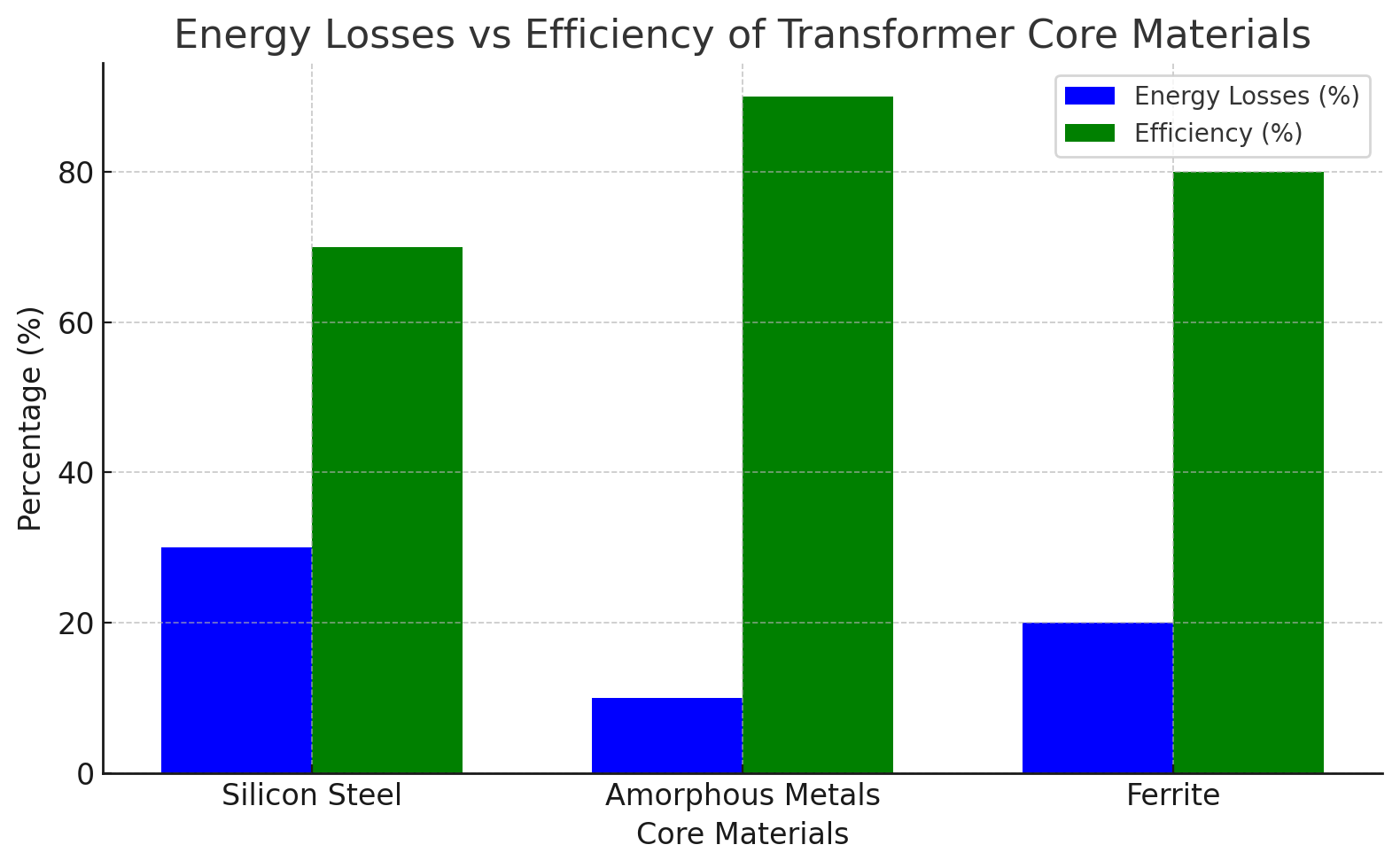
Core Material | Energy Losses | Efficiency Level | Application |
Silicon Steel | Moderate | High | Power transmission, grid systems |
Amorphous Metals | Very Low | Very High | Renewable energy, small transformers |
Ferrite | Low | Moderate | Electronics, high-frequency transformers |
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, transformer cores are playing an increasingly important role in integrating solar and wind power into the grid. Renewable energy sources generate power at varying levels, and transformer cores help manage these fluctuations by adjusting voltage levels and ensuring the steady flow of electricity. Amorphous cores, with their high efficiency, are often used in renewable energy applications to minimize losses and maximize performance.
Efficient transformer cores are critical for integrating renewable energy into the grid, ensuring that power is transmitted effectively without excessive loss or instability. Transformer cores help optimize the operation of solar and wind farms, enabling them to contribute reliably to the overall power grid.
Transformer cores also play a crucial role in smart grid technology and energy storage systems. In modern electrical grids, transformer cores help manage two-way energy flow, support energy storage devices like batteries, and optimize grid performance. This capability allows for more efficient use of energy, particularly in areas with variable renewable energy generation.
Design Feature | Impact on Efficiency | Result |
Lamination Thickness | Thinner laminations reduce eddy current losses | Increased efficiency |
Core Type (Shell vs. Core) | Shell-type reduces leakage, better voltage regulation | Higher efficiency in lower voltage applications |
Use of Amorphous Metals | Low hysteresis and eddy current losses | Significant energy savings |
The future of transformer cores lies in continuous advancements in material science. Nanocrystalline alloys and superconducting materials hold the potential to drastically reduce energy losses and improve transformer efficiency. These new materials promise even greater efficiency, helping transformers handle larger loads while consuming less energy.
While superconducting materials are currently expensive and impractical for large-scale use, their potential to eliminate energy losses entirely makes them an exciting area of research. As technology improves and costs decrease, these materials could become a game-changer in transformer core technology.
In addition to material innovations, improvements in transformer core design are helping create greener and more efficient systems. New design strategies, such as optimizing the geometry of cores and using advanced cooling methods, are helping to reduce losses and improve transformer performance. As global energy demands grow, these innovations will be crucial for meeting the increasing need for sustainable and efficient energy distribution systems.
Transformer cores play a critical role in global energy systems, from power generation to renewable energy integration. They minimize energy loss and improve efficiency. Advances in materials like amorphous metals and nanocrystalline alloys enhance performance and energy savings. As the world shifts to greener energy solutions, transformer cores will be even more vital for efficient power transmission and reducing carbon footprints.
At Shanghai JISCO, we provide high-quality transformer cores that contribute to sustainable energy solutions by improving reliability and efficiency.
A: A transformer core is a magnetic material that helps efficiently transfer electrical energy. It plays a crucial role in reducing energy loss and ensuring the smooth operation of power systems globally.
A: Transformer cores, made from materials like silicon steel and amorphous metals, minimize energy loss by guiding magnetic flux efficiently, making power transmission more effective and energy-saving.
A: Common materials include silicon steel for high efficiency and amorphous metals for energy-saving. These materials reduce energy losses and improve overall performance in power systems.
A: Transformer cores enable the integration of renewable energy sources like solar and wind into the power grid, ensuring efficient transmission despite fluctuating power levels.
A: Amorphous metal cores reduce energy losses by up to 70%, offering greater efficiency in energy transfer compared to traditional silicon steel cores, especially in low-load applications.
A: Efficient transformer core designs, such as core-type and shell-type, help in minimizing losses during power transmission and ensure stable energy distribution to homes and businesses worldwide.